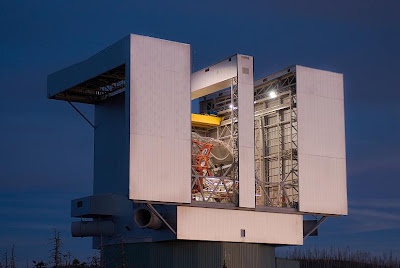
Large Binocular Telescope-Big Bigger Biggest.1.Collecting Light 2.Mirrors 3.Tracking
4.Transporting the Mirror 5.Temperature 6.Atmosphere
The world first reflecting telescope.
Newton's mirror the metal disk polishing into the concave shape down to the bottom, it reflected
the light from the distance object to the single point, the second small mirror then bounced the
light to the eyepiece. Because the light doesn't pass through the lens, there is no separation of
colors and the imagine is not blurred.
By reflecting the light, Newton's telescope produced the sharp imagine. From this point, the
story of how telescopes evolve is the story of mirrors not lens.

It collects the star light falling on the earth bringing them to the focus, so we can grasp the very thin singles from the very distance objects. Size matters. The larger mirror, the more light it can capture. By using the mirrors in tandem the astronomers are able to gather much light.
This is not like the commercial CCD camera that you can buy, it's optimized for very low light.
The CCD chips in the vacuum can, they are cooled in the liquid nitrogen.
Rather than try to collect the light from the whole spectrum, each camera is finally tuned to detect just half of colors. This pictures then combines to produce far higher quality imagines than could ever be made with a single camera.

Creating the parabola glass is simple, as long as you melt the glass first and give it the spin.
The giant rotating furnace, loaded with the glass.
Opticians have to check every Japanese imported glass for flaws.
Centrifugal force pushes the glass into the parabola shape.
The machine is randomly to polish the mirror.
To complete the process, a thin layer alumininum must be applied to each disk to create the
mirror surface.
Engineers place the glass disk inside the giant bell jack, powerful pumps suck out all of the air of the jack to create the vacuum, crucibles on the side of the jack, as the aluminium liquid vaporized, the molecules of aluminium flows through the chamber and condensed on the surface of the glass. Vacuum ensures the molecules spreading evenly across the entire surface
to create the flawless of the reflective mirror.
The biggest challenge for astronomers is keeping this dim light for long enough to get exposure.
A very thin layer of the oil with huge forces holding molecules together, this would be able to
withstand a massive mechanical weight.
But the telescope is much heavy to squeeze out the layer of the oil. Using the high pressure jets
to shoot the oil upward to the telescope, this constantly replenish the squeezed out oil and
provided the thin layer which the telescope can float.
Rather than cooled the whole building, the engineer decided to simply cool the mirror itself.
They take advantage like the honeycomb, built in the back of the mirror, and then they shot the
cold air through the tiny jets into this cavities. This cooled the mirror from the inside keeping
the temperature constantly and preventing the front planes of the mirror bending.
We look at the night sight, we always the stars twinkling. The twinkling is caused by atmospheric
turbulence. That's why put the telescope into the space, totally free from all atmospheric
interference.
The second mirror would counteract the deviation crating the crystal imagines.















































No comments:
Post a Comment